Hooke’s Law
Have you ever noticed when you lie on your bed you don’t fall through it, nor is it hard as wood.
You sink into it, the same way you sink into a chair. This is because some objects squash and stretch.


When you bounce a tennis ball you can see how it changes shape. The ball hits the floor and deforms.
Forces can Compress or Stretch object.
As we know everything in this world is made of atoms. In solids these atoms are close together and held by bonds.
When you step on a solid (like the floor) the bonds between the atoms are compressed.
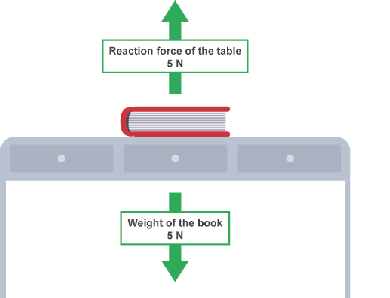
When you stand on the floor, your weight pushes the particles together. The bonds between the atoms are compressed and they begin to push back. Them pushing back, supports you and stops your from falling through.
This support force is called the reaction force.
When your on a trampoline you’ll notice that every time you land the springs stretch. When you bungee jump the cord stretches. The amount that an object stretches is called the extension.
Once a bungee cord has stretches as far as it can, it pulls back. This force is called tension.
Springs are unique, in that, when you apply a force to it, the extension will equal that force.
This is why we use spring to measure forces in a newtonmeter
Once you remove the force the spring goes back to its original length, unless it has past its Elastic limit.
Once it goes past its elastic limit it looses its shape.
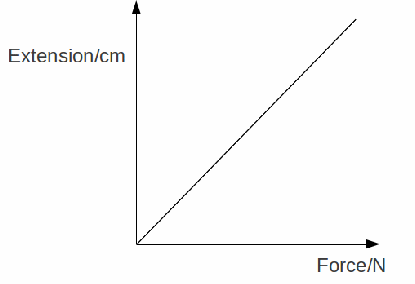
So, if the extension doubles when the force doubles, the object obeys Hook’s law.
You can see this in the graph to the left. As force increases, extension should increase by the same amount.
Hook’s law doesn't apply to everything. Elastic bands and bungee cords don’t always follow this law, like springs.


Question
Short Answer Questions
1. Define the term Deform
2. What is the Reaction force?
3. Copy and Complete the sentence:
Forces can change the shape of objects or ________them. Solid surfaces are made of _______. The bonds between particles are compressed when you apply a force. They _____ back on you. This provides a _____ force called the ______ force.
4. You stand on the edge with a bungee cable tied at your feet. Once you jump state and explain the forces influencing your fall and bounce back. (Include, gravity, air resistance, extension and tension in your explanation) 4 marks.
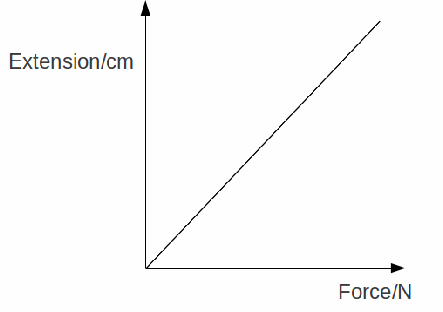
5. Analyse and interpret the graph to the right.
Explain what law this illustrates
6. If a spring is 4cm long at rest, but when a force is added to it, it become 8 cm long, how much extension has occurred and how much force was applied?
7. Explain how your chair pushes you up?
8. Explain how particles in the floor reaction when you step on them